Inflation, Economy and Economics
By: Syeda Sadia Amber Jilani( Columnist, Economist & Economic Analyst)
Inflation has become a dangerous problem for every country, society and even an every person.
The daily increase in the prices of essential commodities is making it increasingly difficult for an economically average person to manage their economic activities. In simpler words, the rising costs of basic necessities are causing financial struggles for ordinary people.
Developing Countries like Pakistan, which are already facing economic challenges alongside numerous other issues, are finding this situation even more distressing. Let’s look at it in simple terms: what is inflation, it’s types and what does Economics say about it? How can we try to control it?”
In Economics, inflation is a sustained increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy over a period of time. Basically, It is a macro-economic phenomenon as well as one of the main problems of developing and under developing countries.
Types of Inflation:
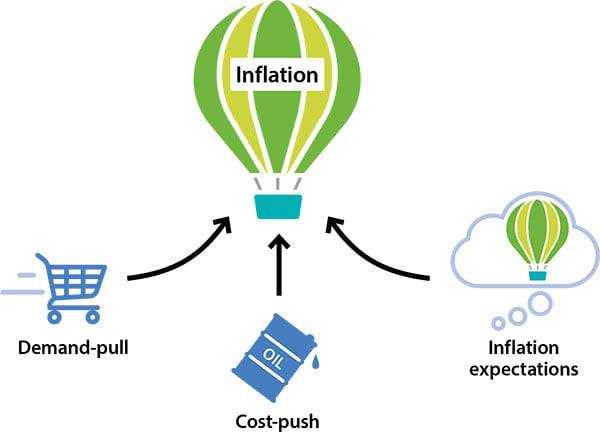
The types or causes of Inflation can be grouped into two main categories:
—>1_ Demand-pull Inflation,(Keynesians Approach); Inflation due to increase in demand , where Aggregate demand is greater than Aggregate Supply at the full employment level and it’s result is Inflation.
—>2_ Cost-push Inflation; Inflation or Higher Prices due to increase in Cost of Production. When the costs of production get rise, the Aggregate Supply Curve shifts to left because of low production. Here is also Aggregate Demand is greater than Aggregate Supply which causes prices to rise. But after some times due to higher prices Aggregate Demand decreases. High prices and slow growth lead towards unemployment.
The Extreme condition of Cost-push Inflation is called “Stagflation” . In that condition, higher inflation relates to higher unemployment (The Opposite Situation of Phillips Curve, PC). Sometimes expected inflation in future is also the cause of Inflation.
Measurement of Inflation; The most well-known indicator of inflation is the Consumer Price Index (CPI), which measures the percentage change in the price of a basket of goods and services consumed by households.
Formula:
Inflation Ratio =P2 _P1/P1×100 In inflation the purchasing power of households Or Consumers is decreased, And the quantity demanded by consumers also declines. Consumers are forced to spend much more money for the same basket of goods and services. So, we can say that Inflation has multiplier effects not only on individual’s budget but also on the whole economy like unemployment, devaluation of our currency, poverty, Increase in foreign Loans and interests. Moreover, it is also harmful for growth.
How to Control Inflation:
There are two main methods or Ways to Control Inflation.
1- Monetary Policy by Central Bank: The most important and commonly used method to control inflation is contractionary monetary policy of the Central Bank. Mostly The Central Bank of a Country uses high interest rates and lowering the prices of bonds and securities (in open makertopration) to reduce the money supply in the economy. Thus, consumption falls, Aggregate Demand decreases, prices fall and inflation slows down.
2-Fiscal policy by Govt: Strict or Contractionary Fiscal policy by the government is also a method to control inflation in which it might raise taxes and decrease government spending to reduce money supply and consumption level of the Economy that can make the result of falling prices and reducing Inflation.
………………